

When Thorndike placed his cats in a puzzle box, he found that they learned to engage in the important escape behavior faster after each trial.
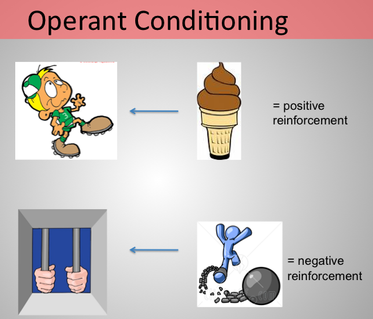
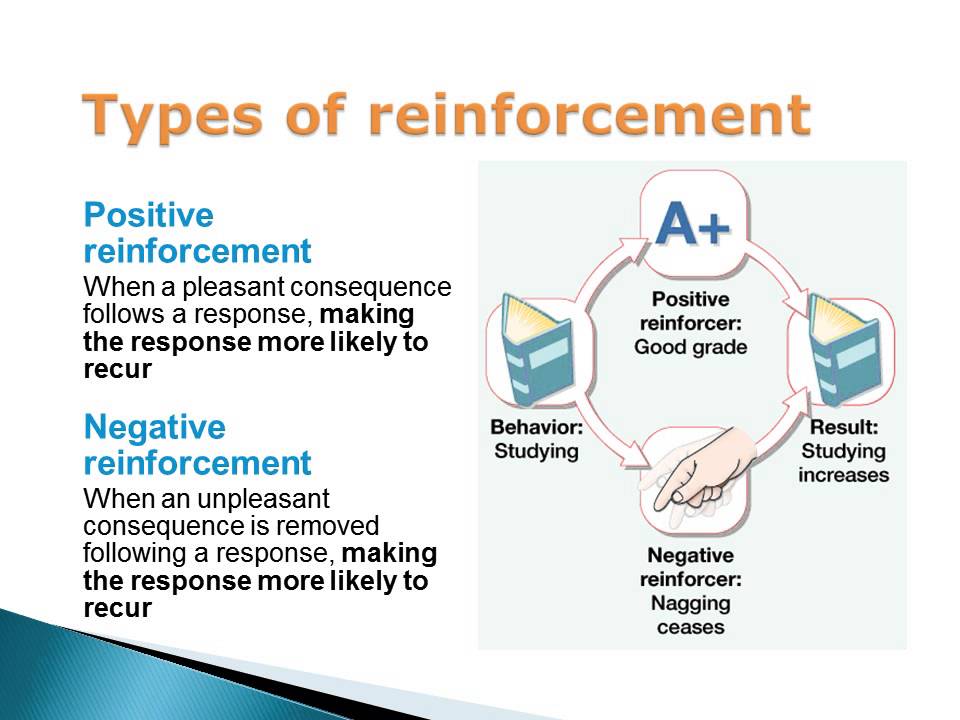
Unsuccessful responses, which produce unpleasant experiences, are “stamped out” and subsequently occur less frequently. The essence of the law of effect is that successful responses, because they are pleasurable, are “stamped in” by experience and thus occur more frequently. Observing these changes in the cats’ behavior led Thorndike to develop his law of effect, the principle that responses that create a typically pleasant outcome in a particular situation are more likely to occur again in a similar situation, whereas responses that produce a typically unpleasant outcome are less likely to occur again in the situation (Thorndike, 1911). The next time the cat was constrained within the box it attempted fewer of the ineffective responses before carrying out the successful escape, and after several trials the cat learned to almost immediately make the correct response. But eventually, and accidentally, they pressed the lever that opened the door and exited to their prize, a scrap of fish.
#Positive reinforcement negative reinforcement examples how to#
At first the cats scratched, bit, and swatted haphazardly, without any idea of how to get out. In his research Thorndike (1898) observed cats who had been placed in a “puzzle box” from which they tried to escape ( Note 7.21 “Video Clip: Thorndike’s Puzzle Box”). Thorndike (1874–1949) was the first scientist to systematically study operant conditioning. How Reinforcement and Punishment Influence Behavior: The Research of Thorndike and Skinner


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
